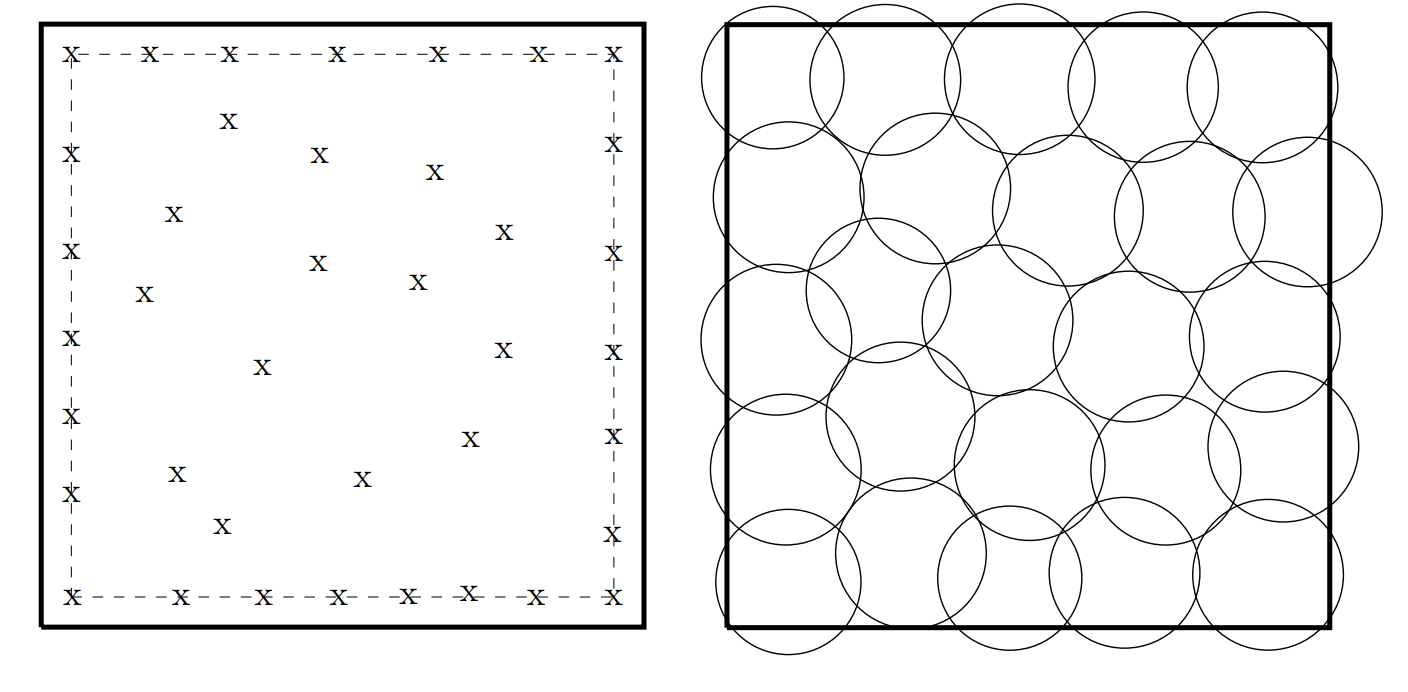
This repository contains the metameric evolutionary algorithm used in my dissertation Metameric Representations in Evolutionary Algorithms. Metameric problems are ones which use a genome that is at least partially segmented into a number of metavariables. For example, a wind farm might be defined as a number of turbines or a coverage network by a number of nodes. Two example solutions to these problems are shown below.
For more information on metameric representations please see the following. The documentation here frequently refers to certain chapters or sections in the dissertation.
Ryerkerk, M., Metameric Representations in Evolutionary Algorithms (2018), PhD Dissertation
This code was written such that new evolutionary operators or optimization problems can be easily added. Each folder here has an additional readme.md file that provides additional information on the functions it contains.
MATLAB 2018a was used to run all the trials used in the dissertation. RNG seeds are used for each study/trial that should allow the results from the dissertation to be replicated.
The trials from the dissertation can be found in setups/dissertation_setups/, running any of these scripts should begin the associated study. More information on how the setup scripts are structured can be round in setups/readme.md.
New crossover, mutation, selection, and filter/repair operators can be added with minimal modification to the code. First, write the operator using a function signature that matches those of the provided functions. Then, include the function's handle to the appropriate field in the params structure. Generally these are set in either the problem or algorithm scripts in setups/ If desired you can write additional, operator-specific fields to the params and outputs structures.
As with operators, new problems and evaluation functions can be created with minimal modification. An evaluation function is required, further details are provided in evaluation/readme.md. A new problem setup must then be created containing the design variables, objectives, and constraints for this problem. Instructions are given in setups/readme.md. You can then define and run a study on the newly defined problem.
Two important structures are passed to almost all function calls in this code: params and outputs.
The following set of parameters needs to be set at the start of the run and will remain fixed. It is possible to alter these during a run (e.g., updating the mutation rate each generation), but this is not done in any of the provided code. Some parameters are specific to certain functions, and will not need to be defined if that function is not used.
params.saveNamename of the study, will be used when saving resultsparams.objListarray of objective objects. Note that only single-objective selection operators are provided.params.conListarray of constraint objects.params.varListarray of variable objects.params.evaluationFunctionfunction handle to the evaluation function.params.evalLimitnumber of evaluations that will be used each trial.params.numTrialnumber of independent trials to run for this problem setup.params.popSizepopulation sizeparams.rngValvalue used to seed random number generator. Each trial will used a different random seed, but this value affects the seeds used.params.orderedProblemset to 1 if the problem is an ordered one (Sections 2.2.1, 4.1.2) and 0 otherwise. The dissimilarity function, mutation operator, and some crossover operators will function differently for ordered problems.params.minInitialMetavariablesminimum number of metavariables allowed in initial population. Also used as bounds for fixed selection window, if used.params.maxInitialMetavariablesmaximum number of metavariables allowed in initial population. Also used as bounds for fixed selection window, if used.params.hiddenMetavariableset to 1 if a hidden-metavariable representation (Section 5.2.1) is to be used.params.staticMetavariableset to 1 if a static-metavariable representation (Section 5.2.2) is to be used.params.staticGenotypethe static-genotype (Section 5.2.2), only required if static-metavariable representation is used.params.hiddenGenomeLengthlength of genome if hidden- or static-metavariable representation is used. Only required of one of these is used.
params.crossoverOperatorfunction handle to the crossover operator.params.crossoverRatecrossover rate, in range [0, 1].params.pairingOperatorfunction handle to the parent pairing operator.params.mutationOperatorfunction handle to the mutation operator.params.mutationMagnitudedesign variable mutation magnitudes are sampled from a normal distribution, whose standard deviation is equal to this value multiplied by the range of the mutated variable. Smaller values will result in smaller mutations.params.addMetavariableMutateChancechance that a randomly generated metavariable is added to a genome during mutation, in range [0, 0.05].params.removeMetavariableMutateChancechance that a random metavariable is removed from a genome during mutation, in range [0, 0.05].params.permutationChancechance that two randomly selected metavariables in a genome exchange positions during mutation, in range [0, 0.05].params.spatialVariablesindices of variables inparams.objListthat are used by the spatial crossover operator. Only required if spatial crossover is used.
params.selectionOperatorfunction handle to selection operator.params.windowFunctionfunction handle to window function, required only if a length niching selection operator is used.params.windowRangewidth of window, used by moving or biased windows.params.BDecayRatedecay rate used by biased window function (Section 7.2.4)params.FDecayRatedecay rate used to calculate trend in fitness of best solutions (Section 7.3.2.3). Only required if score selection is used.params.localSelectionOperatorlocal selection operator applied to each niche, or entire population if non-niching selection is used. See Section 7.3.
These values are not by the user. Some are determined at the start of the trial, while others will be updated over the course of the trial.
params.trialNumberthe current trial being run, will be between 1 andparams.numTrial.params.rngSeedthe random seed used by the current trial. All trials in a study will have a different seed,parmas.rngValis used to calculate the seed.params.curGencurrent generation of the trial.params.curEvalCountnumber of evaluations used so far.params.currentWindowlengths present in current selection window.
This structure tracks certain values throughout a single trial, such as best solution length or objective value. Some values will be used by certain operators, for example to calculate the change in best solution length each generation. Others are only for debugging or post processing purposes. Certain fields will only be present when particular operators are used.
outputs.bestFitobjective function value of best solution at each generation.outputs.bestLengthlength of best solution at each generation.outputs.bestPenpenalty (from constraint violations) of best solution at each generation.outputs.popHistcontains the fitness, penalty, and length of all solutions selected at each generation.outputs.winStartlower bound of selection window at each generation.outputs.winEndlower bound of selection window at each generation.outputs.Bbias factor used by biased window at each generation (Section 7.2.4)outputs.Ffitness trend value at each generation (Section 7.3.2.3).outputs.dHistthe average distance between solutions selected in each niche at each generation(i.e., outputs.dHist(generation, length)). Will be set to 0 if that niche doesn't exist for a given generation. Only
This code was written to be run in parallel such that many trials of the same study can be run simultaneously. If you open a parpool and change the outermost loop of MEA.m to parfor w = 1:params.numTrial it should work, and the results from running in parallel should match those of a non-parallel run.
Alternatively, if you have an expensive evaluation function it is beneficial to evaluate all solutions in the population in parallel. This requires editing EvaluatePopulation.m to make it parallel friendly.
Any trial that finishes will be saved to saved_trials/{params.saveName}/{params.saveName + '_' params.trialNumber}.mat. The number of files produced by a complete study will be equal to params.numTrial.
Before running a trial the code will check if this particular trial for this particular study has already been completed. If so it will skip that trial. For this reason it is important to change params.saveName, or delete the existing .mat files, before starting a new study.
The current code does not provide functionality for saving or resuming incomplete trials.