-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 2
Cura engine source code analysis
The code analysis is done on Cura engine the last commit on the legacy branch. I used lxr cross referencer at home. The URLs of quoted source code have been removed. It only shows source code relative file path and also its line number in the commit 4621d77a17403b009c4.
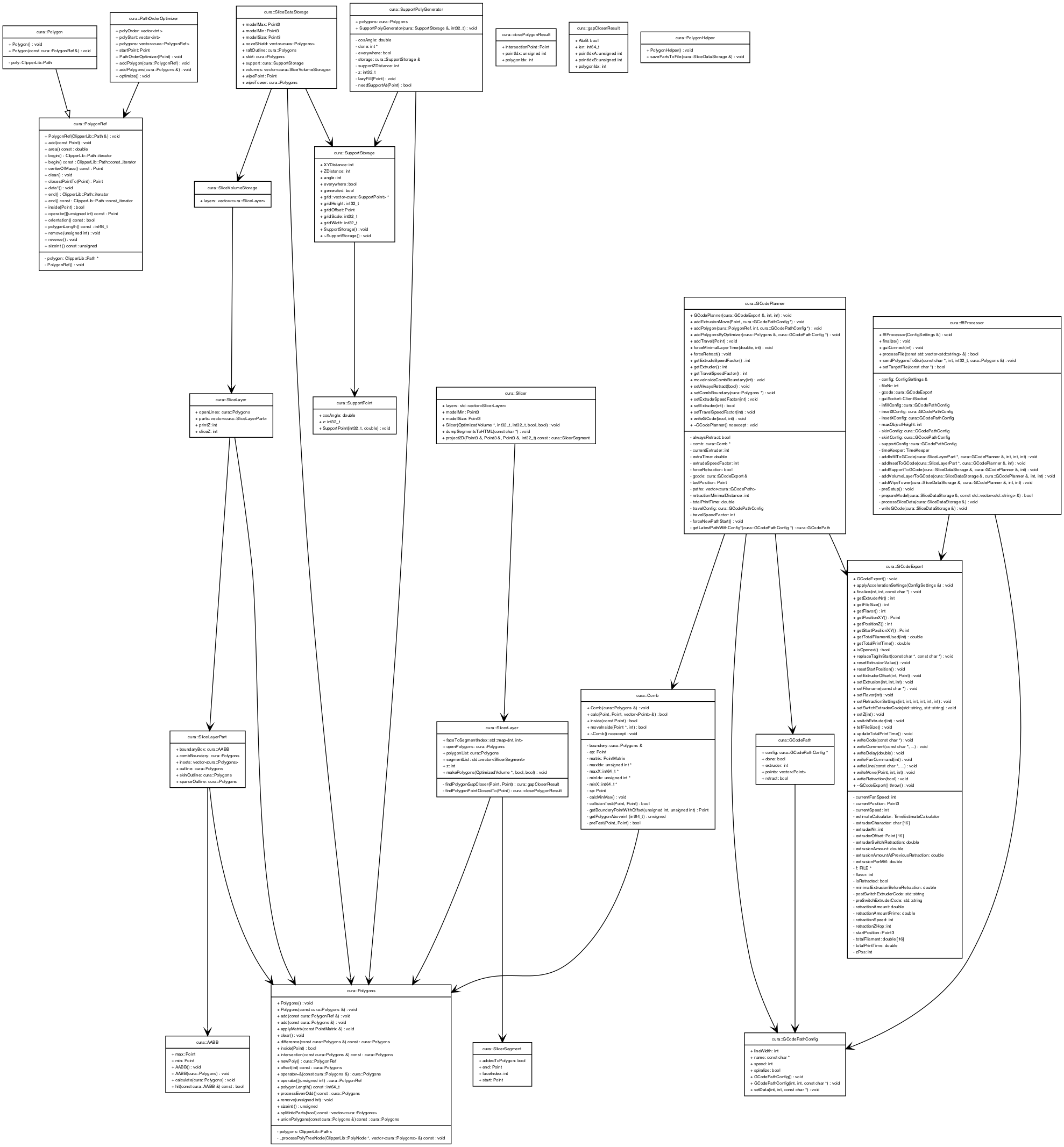
- Key Data Structure and Class of Cura Engine
- Entry point of Cura Engine
- fffProcessor::processFile
-
Overview of fffProcessor::processFile
- Part I. Create SliceDataStorage key data structure
- Part II. fffProcessor::preSetup
- Part III. fffProcessor::prepareModel
- Part IV. fffProcessor::processSliceData
-
Part V. fffProcessor::writeGCode
- Overview
- Key data structure
- Algorithm of fffProcesor::writeGCode
- fffPorcesor::addSupportToGCode
- fffProcessor::addVolumeLayerToGCode
- fffProcessor::addInfillToGcode (called by addVolumeLayerToGCode)
- fffProcessor::addInsetToGcode (called by addVolumeLayerToGCode)
- GCodePlanner::writeGCode
- [TODO] GCodePlanner::moveInsideCombBoundary
- [TODO] PathOrderOptimizer::optimize
For key data structure, please refer to src/sliceDataStorage.h. Below is UML class diagram:
- Send feedback to GUI by socket
- Main program to gluing the whole slicing pipeline from loading STL model, slicing, path planning to G code generation.
-> has a vector of SliceVolumeStorage (per each volume)
Note: the whole pipeline passed this data structure!
-> has a vector of SliceLayer (per each layer in the volume)
-> has a vector of SliceLayerPart (per each part in the layer)
- boundaryBox: AABB => TODO
- outline: Polygons => a vector closed polygon array of the part. The first polygon is outermost one, while the rest is inner one.
- combBoundery: TODO
- insets: vector => for each part, there are only one outer perimeter but there might be zero or one or more than one inner perimeters depending the structure. Thus, it use a vector of Polygons (note that this is NOT Polygon)
- skinOutline: TODO
- sparseOuline: TODO
0019 class SliceLayerPart
0020 {
0021 public:
0022 AABB boundaryBox;
0023 Polygons outline;
0024 Polygons combBoundery;
0025 vector<Polygons> insets;
0026 Polygons skinOutline;
0027 Polygons sparseOutline;
0028 };=> has a pointer to ClipperLib::Path
=> is sub class of PolygonRef
=> has an object of ClipperLib::Path
=> has an object of ClipperLib::Paths
- Has a GCodeExport reference
- Has a vector of GCodePath
- Has a GCodePathConfig for travel path
- Has a Comb object (?)
- Planning path for specific type, eg inner wall, outer wall, infill and etc.
- This class instructs path planning!!! You may get last position/start position.
- Generate G code
- Keep physical information such as # of extruder, current /last position of nozzle and etc
- Estimate print time
- config: cura::GCodePathConfig ⇒ a GCodePathConfig pointer
- done: bool ⇒ A boolen flag done to indicate if path planning is done or not for this path.
- extruder: int ⇒ An assigned index of extruder
- points: vector ⇒ Point in the planned paths
- retract: bool ⇒ A boolean flag to indicate if reaction is enabled or not.
Specify configuration printing speed, extrusion line width and is spiralize.
0110 //The GCodePathConfig is the configuration for moves/extrusion actions. This defines at which width the line is printed and at which speed.
0111 class GCodePathConfig
0112 {
0113 public:
0114 int speed;
0115 int lineWidth;
0116 const char name;
0117 bool spiralize;
...- startPoint: Point =>
- Polygons: vector => input to store PolygonRef into vector
- polyStart: vector => the starting point of the point index of each polygon by optimized order of Polygons. Eg, polyStart[0] =3, refer to the starting point at the 3rd point in the polygon - pathOrderOptimizer.Polygons[polyOrder[0]]. Note that it is not the original order.
- polyOrder: vector => store the index number of sorted polygons result. Eg polyOrder[0] = 3, the optimized order of index 0 is pathOrderOptimizer.Polygons[3].
See src/pathOrderOptimizer.h#0010
0012 public:
0013 Point startPoint;
0014 vector<PolygonRef> polygons;
0015 vector<int> polyStart;
0016 vector<int> polyOrder;src/main.cpp
main.cpp jumps to fffProcessor::processFile
src/fffProcessor.h#0068
0068 bool processFile(const std::vector<std::string> &files)
0069 {
0070 if (!gcode.isOpened())
0071 return false;
0072
0073 TimeKeeper timeKeeperTotal;
0074 SliceDataStorage storage;
0075 preSetup();
0076 if (!prepareModel(storage, files))
0077 return false;
0078
0079 processSliceData(storage);
0080 writeGCode(storage);
0081
0082 cura::logProgress("process", 1, 1);//Report the GUI that a file has been fully processed.
0083 cura::log("Total time elapsed %5.2fs.\n", timeKeeperTotal.restart());
0084 guiSocket.sendNr(GUI_CMD_FINISH_OBJECT);
0085
0086 return true;
0087 }- Create key data structure SliceDataStorage.
- fffProcessor::preSetup -- load setting
- fffProcessor::preparemodel -- load STL file and slice the model. Upon finishing, it generate sliced layer and parts in each layer.
- fffProcessor::processSliceData -- extra processing, such as top/down skin
- fffProcessor::writeGCode -- generate G code
We will explore each of the bullet point in details.
See Key Data Structure and Class of Cura Engine section.
No interesting thing here.
src/fffProcessor.h#0114
- Load STL life and optimize model
- Slice object model.
- Generate support map
- Generate layers part
src/fffProcessor.h#0190
Create a Slicer object:
0186 cura::log("Slicing model...\n");
0187 vector<Slicer> slicerList;
0188 for(unsigned int volumeIdx=0; volumeIdx < optimizedModel->volumes.size(); volumeIdx++)
0189 {
0190 Slicer slicer = new Slicer(&optimizedModel->volumes[volumeIdx], config.initialLayerThickness - config.layerThickness / 2, config.layerThickness, config.fixHorrible & FIX_HORRIBLE_KEEP_NONE_CLOSED, config.fixHorrible & FIX_HORRIBLE_EXTENSIVE_STITCHING);
0191 slicerList.push_back(slicer);
0192 for(unsigned int layerNr=0; layerNr<slicer->layers.size(); layerNr++)
0193 {
0194 //Reporting the outline here slows down the engine quite a bit, so only do so when debugging.
0195 //sendPolygonsToGui("outline", layerNr, slicer->layers[layerNr].z, slicer->layers[layerNr].polygonList);
0196 sendPolygonsToGui("openoutline", layerNr, slicer->layers[layerNr].z, slicer->layers[layerNr].openPolygons);
0197 }
0198 }Inside Slicer class constructors, it get the following done:
- Compute number of layers, given layer height
- Slice triangle mesh in each layer
- Get the set of line segments in each layer, which is intersection of slicing plan and triangle mesh (if any)
- Find the closed polygons from line segments.
src/fffProcessor.h#0209
0209 cura::log("Generating layer parts...\n");
0210 for(unsigned int volumeIdx=0; volumeIdx < slicerList.size(); volumeIdx++)
0211 {
0212 storage.volumes.push_back(SliceVolumeStorage());
0213 createLayerParts(storage.volumes[volumeIdx], slicerList[volumeIdx], config.fixHorrible & (FIX_HORRIBLE_UNION_ALL_TYPE_A | FIX_HORRIBLE_UNION_ALL_TYPE_B | FIX_HORRIBLE_UNION_ALL_TYPE_C));
0214 delete slicerList[volumeIdx];
0215
0216 //Add the raft offset to each layer.
0217 for(unsigned int layerNr=0; layerNr<storage.volumes[volumeIdx].layers.size(); layerNr++)
0218 storage.volumes[volumeIdx].layers[layerNr].printZ += config.raftBaseThickness + config.raftInterfaceThickness;
0219 }⇒
src/layerPart.cpp#0052
0052 void createLayerParts(SliceVolumeStorage& storage, Slicer slicer, int unionAllType)
0053 {
0054 for(unsigned int layerNr = 0; layerNr < slicer->layers.size(); layerNr++)
0055 {
0056 storage.layers.push_back(SliceLayer());
0057 storage.layers[layerNr].sliceZ = slicer->layers[layerNr].z;
0058 storage.layers[layerNr].printZ = slicer->layers[layerNr].z;
0059 createLayerWithParts(storage.layers[layerNr], &slicer->layers[layerNr], unionAllType);
0060 }
0061 }⇒
src/layerPart.cpp#0021
0021 void createLayerWithParts(SliceLayer& storageLayer, SlicerLayer layer, int unionAllType)Summary:
- Loop through each layer
- Create parts (island) in each layer by clipping closed polygons Upon finishing slicing, object is sliced by layers and clipper has parts on each layers.
src/fffProcessor.h#0224
TODO - give a summary.
src/fffProcessor.h#0338
Line 0338-0434: Ignore analysis for G code setup.
src/fffProcessor.h#0434
Starting from line 0434:
TODO - give a summary.
- gcode is an object of the class GCodeExport. It is a private member in fffProcessor
- Several xxxConfig are objects of the class GCodePathConfig. They are private members in fffProcessor
- In each layer loop in fffProcessor.writeGCode, create an object gcodeLayer of class GCodePlanner within each layer loop. See its constructor --
GCodePlanner::GCodePlanner(GCodeExport& gcode, int travelSpeed, int retractionMinimalDistance). Search GCodePlanner insider the method. There are several places to construct GCodePlanner in the stack.
One of places:
src/fffProcessor.h#0468
0468 GCodePlanner gcodeLayer(gcode, config.moveSpeed, config.retractionMinimalDistance);Loop through each layer:
-
Set extrusionWidth, special treatment for layer 0
-
Setup config per each type -- GCodePathConfig object defined in class fffProcessor
- 0025 GCodePathConfig skirtConfig;
- 0026 GCodePathConfig inset0Config;
- 0027 GCodePathConfig insetXConfig;
- 0028 GCodePathConfig infillConfig;
- 0029 GCodePathConfig skinConfig;
- 0030 GCodePathConfig supportConfig;
-
setExtrusion based on layer index
-
Create an object gcodeLayer of class GCodePlanner. One GCodePlanner object per each layer.
-
Set position of z axis
-
Reset x, y position to INT32_MIN (-2147483648)
-
If print support first, call addSupportToGCode first and then call addVolumeLayerToGCode. Otherwise, reverse the calling order. (src/fffProcessor.h#0711)
-
Loop through each volume, call addVolumeLayerToGCode to generate path. (src/fffProcessor.h#0526)
-
If print support after print the volume, call addSupportToGCode now.
-
Call GCodePlanner::forceMinimalLayerTime. (src/gcodeExport.cpp#0556) Calculate total time spent on this layer = extrude time + travel time. If time less than desired limit, slow down the print speed.
-
Determine fan speed
-
Call GCodeExport gcode.writeFanCommand to output M code to control fan speed
-
Call GCodePlanner gcodeLayer.writeGCode to output G code. The paths already generated in GCodePlanner.paths : vector. Loop through each path to generate actual GCode. See GCodePlanner::writeGCode!!! (src/gcodeExport.cpp#0608)
End of writeGocde.
src/fffProcessor.h#0711 TOOD: read this later.
Start at
src/fffProcessor.h#0526
Ignore simple setting
http://192.168.2.213/lxr/source/curaengine/src/fffProcessor.h#0590 First, sort parts order with PathOrderOptimizer. But the starting point doesn’t make any sense.
TODO Boy, we are going to improve this here!!!
See comment code:
// TODO: need to figure it out how gcode.getStartPositionXY get udated.
0590 PathOrderOptimizer partOrderOptimizer(gcode.getStartPositionXY());
0591 for(unsigned int partNr=0; partNr<layer->parts.size(); partNr++)
0592 {
// insets[0] refer to the outer perimeter
// inset[0][0] refer to the first closed polygon of the outer perimeter
// Sort the polygon -- inset[0][0] of all parts
0593 partOrderOptimizer.addPolygon(layer->parts[partNr].insets[0][0]);
0594 }
0595 partOrderOptimizer.optimize();For details see PathOrderOptimizer::optimize.
First, sort parts order with PathOrderOptimizer. The starting point doesn’t make any sense. TODO Boy, we are going to improve this here!!!
Loop through each part by the optimized order of PathOptimizer:
- Determine comb and always retract setting
- Set fill angle and extrusionWidth according to the layer
- Depending on the printing order of perimeter and infill, run the following by order accordingly:
- addInfillToGCode (src/fffProcessor.h#0651)
- addInsetToGCode (src/fffProcessor.h#0690)
- Logic related to path generation of skin (a.k.a top/bottom layers). Use input data part->skinOutline and function generateLineInfill to generate skin.
- If enable combing == no skin, set always retraction true and set gcodeLayer->comb as nullptr
- Sort skinPolygons polygons by gcodeLayer.addPolygonsByOptimzers
- Line 0645: combing prevent retract on the perimeter. Some logic to force path change. GCodePlanner gcodeLayer.moveInsideCombBoundary.(src/gcodeExport.cpp#0512) TODO: read GCodePlanner::moveInsideCombBoundary!!!
End of looping part
Reset gcodeLayer.setCombBoundary(nullptr)
End of addVolumeLayerToGCode
Summary:
generate the paths of infill and store them into gcodeLayer reference passed from the caller.
src/fffProcessor.h#0651
0651 void addInfillToGCode(SliceLayerPart part, GCodePlanner& gcodeLayer, int layerNr, int extrusionWidth, int fillAngle)- 1st argument part passed in from the loop. It contains geometry of infill area.
- 2nd argument gcodeLayer passed from layer loop stores generated path.
Inside fffProcessor::addInfillToGcode:
- A Polygons object infillPolygons are created in the method.
- There are 4 different types of infill patterns available: automatic(default), grid, line and concentric.
- For each infill pattern method:
- Input is parts->sparseOutline
- Output is infillPolygons
- Then pass generated path infillPolygons into GCodePlanner gcodeLayer.addPolygonsByOptimizer to sort and add infillPolygons into GCodePlanner with infillConfigs. See below:
Summary:
- Optimize the path planning order of infill paths infillPolygons in the forms of Polygons
- Loop through each ordered path in the optimized order.
- Update GCodePlanner.paths with specific starting point of the path and also corresponding PathConfig.
See my commented code below:
src/gcodeExport.cpp#0543
0543 void GCodePlanner::addPolygonsByOptimizer(Polygons& polygons, GCodePathConfig config)
0544 {
// initialize optimizer starting point with lastPosition
// the optimized output result is:
// PathOrderOptimizer::polyOrder -- the order of ploygon
// PathOrderOptimizer.polyStart -- the starting point of polygon
0545 PathOrderOptimizer orderOptimizer(lastPosition);
0546 for(unsigned int i=0;i<polygons.size();i++)
0547 orderOptimizer.addPolygon(polygons[i]);
0548 orderOptimizer.optimize();
0549 for(unsigned int i=0;i<orderOptimizer.polyOrder.size();i++)
0550 {
// PathOrderOptimizer.polyOrder array store the index number of sorted polygons result.
0551 int nr = orderOptimizer.polyOrder[i];
// PathOrderOptimier.polyStart stores the index of starting point in the polygon
0552 addPolygon(polygons[nr], orderOptimizer.polyStart[nr], config);
0553 }
0554 }src/gcodeExport.cpp#0529
0529 void GCodePlanner::addPolygon(PolygonRef polygon, int startIdx, GCodePathConfig config)
0530 {
0531 Point p0 = polygon[startIdx];
// This methods add Point P into last path of GCodePlanner::paths vector with travel config.
// It also determine if retraction is needed.
0532 addTravel(p0);
// loop through the point of the infill polygon starting from the point with index startIdx.
0533 for(unsigned int i=1; i<polygon.size(); i++)
0534 {
0535 Point p1 = polygon[(startIdx + i) % polygon.size()];
//
0536 addExtrusionMove(p1, config);
0537 p0 = p1;
0538 }
0539 if (polygon.size() > 2)
0540 addExtrusionMove(polygon[startIdx], config);
0541 }Summary:
- Append the starting point of the plan path to the last path of GCodePlanner::paths vector with travel config.
- It is more likely that addTravel will create a new GCodePath object.
- Determine if retraction is needed.
- Update GCodePlanner.lastPosition
See my commented code below:
src/gcodeExport.cpp#0474
0474 void GCodePlanner::addTravel(Point p)
0475 {
// This method either creates a new path in GCodePlanner::paths vector if the provided travel config is different from travel config of the last path.
// Otherwise, just append the point into the back of the existing path, which is the last element of GCodePlanner::paths vector.
0476 GCodePath path = getLatestPathWithConfig(&travelConfig);
0477 if (forceRetraction)
0478 {
0479 if (!shorterThen(lastPosition - p, retractionMinimalDistance))
0480 {
0481 path->retract = true;
0482 }
0483 forceRetraction = false;
0484 }else if (comb != nullptr)
0485 {
0486 vector<Point> pointList;
// TODO -- read comb->calc
0487 if (comb->calc(lastPosition, p, pointList))
0488 {
0489 for(unsigned int n=0; n<pointList.size(); n++)
0490 {
0491 path->points.push_back(pointList[n]);
0492 }
0493 }else{
0494 if (!shorterThen(lastPosition - p, retractionMinimalDistance))
0495 path->retract = true;
0496 }
0497 }else if (alwaysRetract)
0498 {
0499 if (!shorterThen(lastPosition - p, retractionMinimalDistance))
0500 path->retract = true;
0501 }
0502 path->points.push_back(p);
0503 lastPosition = p;
0504 }src/gcodeExport.cpp#0506
Summary: For the points other than the starting point of the path, just append the point to the back of path and update GCodePlanner.lastPosition
0506 void GCodePlanner::addExtrusionMove(Point p, GCodePathConfig config)
0507 {
0508 getLatestPathWithConfig(config)->points.push_back(p);
0509 lastPosition = p;
0510 }src/gcodeExport.cpp#0436
0436 GCodePath GCodePlanner::getLatestPathWithConfig(GCodePathConfig config)
0437 {
0438 if (paths.size() > 0 && paths[paths.size()-1].config == config && !paths[paths.size()-1].done)
0439 return &paths[paths.size()-1];
0440 paths.push_back(GCodePath());
0441 GCodePath ret = &paths[paths.size()-1];
0442 ret->retract = false;
0443 ret->config = config;
0444 ret->extruder = currentExtruder;
0445 ret->done = false;
0446 return ret;
0447 }src/infill.cpp#0019
The logic is actually hard coded:
lineSpacing = config.sparseInfillLineDistance = 5 extrusionWidth
0043 SETTING(sparseInfillLineDistance, 100 extrusionWidth / 20);
The logic always choose grid over line due to default value and formula above.
0023 if (lineSpacing > extrusionWidth 4)
0024 {
0025 generateGridInfill(in_outline, result, extrusionWidth, lineSpacing,
0026 infillOverlap, rotation);
0027 }
0028 else
0029 {
0030 generateLineInfill(in_outline, result, extrusionWidth, lineSpacing,
0031 infillOverlap, rotation);
0032 }src/infill.cpp#0035
It generate path with two set of lines by generateLineInfill, one of which are rotate 90 degree from the original rotation.
src/infill.cpp#0053 TODO: read details if necessary
void generateLineInfill(const Polygons& in_outline, Polygons& result, int extrusionWidth, int lineSpacing, int infillOverlap, double rotation)Summary: Inset a.k.a inner and outer wall. It is created in fffProcessor::processSliceData generate insect section. Here we only need to call GCodePlanner::addPolygonsByOptimizer to add path into GCodePlanner.
See my commented code below:
src/fffProcessor.h#0690
0690 void addInsetToGCode(SliceLayerPart part, GCodePlanner& gcodeLayer, int layerNr)
0691 {
0692 if (config.insetCount > 0)
0693 {
0694 if (config.spiralizeMode)
0695 {
0696 if (static_cast<int>(layerNr) >= config.downSkinCount)
0697 inset0Config.spiralize = true;
0698 if (static_cast<int>(layerNr) == config.downSkinCount && part->insets.size() > 0)
0699 gcodeLayer.addPolygonsByOptimizer(part->insets[0], &insetXConfig);
0700 }
0701 for(int insetNr=part->insets.size()-1; insetNr>-1; insetNr--)
0702 {
0703 if (insetNr == 0)
0704 gcodeLayer.addPolygonsByOptimizer(part->insets[insetNr], &inset0Config);
0705 else
0706 gcodeLayer.addPolygonsByOptimizer(part->insets[insetNr], &insetXConfig);
0707 }
0708 }
0709 }- GCodePlanner::writeGCode is to output real GCode command by the GCodePlanner::paths.
- GCodePlanner::writeGCode is called in a couple places in fffProcessor::writeGCode method. But it should invoked if and only if all GCodePlanner::paths all get sorted out.
See code:
src/gcodeExport.cpp#0608
0608 void GCodePlanner::writeGCode(bool liftHeadIfNeeded, int layerThickness)Assuming GCodePlanner::paths is ready.
Loop through each path in the vectors GCodePlanner::paths
- If extruder is different from path->extruder, switch it.
- If path->retract is true, enable retraction
- Update local pointer lastConfig, if path->config changes GCodePlanner::travelConfig
- Nitty gritty determine extrusion speed (src/gcodeExport.cpp#0631)
Now continue to look at the code with the comment:
// special handling to the case where path only contain **ONE** point
0636 if (path->points.size() == 1 && path->config != &travelConfig && shorterThen(gcode.getPositionXY() - path->points[0], path->config->lineWidth * 2))
0637 {
0638 //Check for lots of small moves and combine them into one large line
0639 Point p0 = path->points[0];
0640 unsigned int i = n + 1;
0641 while(i < paths.size() && paths[i].points.size() == 1 && shorterThen(p0 - paths[i].points[0], path->config->lineWidth * 2))
0642 {
0643 p0 = paths[i].points[0];
0644 i ++;
0645 }
0646 if (paths[i-1].config == &travelConfig)
0647 i --;
0648 if (i > n + 2)
0649 {
0650 p0 = gcode.getPositionXY();
0651 for(unsigned int x=n; x<i-1; x+=2)
0652 {
0653 int64_t oldLen = vSize(p0 - paths[x].points[0]);
0654 Point newPoint = (paths[x].points[0] + paths[x+1].points[0]) / 2;
0655 int64_t newLen = vSize(gcode.getPositionXY() - newPoint);
0656 if (newLen > 0)
0657 gcode.writeMove(newPoint, speed, path->config->lineWidth * oldLen / newLen);
0658
0659 p0 = paths[x+1].points[0];
0660 }
0661 gcode.writeMove(paths[i-1].points[0], speed, path->config->lineWidth);
0662 n = i - 1;
0663 continue;
0664 }
0665 }
0666
// special case handling for spiralized path
0667 bool spiralize = path->config->spiralize;
0668 if (spiralize)
0669 {
0670 //Check if we are the last spiralize path in the list, if not, do not spiralize.
0671 for(unsigned int m=n+1; m<paths.size(); m++)
0672 {
0673 if (paths[m].config->spiralize)
0674 spiralize = false;
0675 }
0676 }
0677 if (spiralize)
0678 {
0679 //If we need to spiralize then raise the head slowly by 1 layer as this path progresses.
0680 float totalLength = 0.0;
0681 int z = gcode.getPositionZ();
0682 Point p0 = gcode.getPositionXY();
0683 for(unsigned int i=0; i<path->points.size(); i++)
0684 {
0685 Point p1 = path->points[i];
0686 totalLength += vSizeMM(p0 - p1);
0687 p0 = p1;
0688 }
0689
0690 float length = 0.0;
0691 p0 = gcode.getPositionXY();
0692 for(unsigned int i=0; i<path->points.size(); i++)
0693 {
0694 Point p1 = path->points[i];
0695 length += vSizeMM(p0 - p1);
0696 p0 = p1;
0697 gcode.setZ(z + layerThickness * length / totalLength);
0698 gcode.writeMove(path->points[i], speed, path->config->lineWidth);
0699 }
0700 }else{
// this is the common case, just print the path of the vector GCodePlanner::paths with speed and line width from config.
0701 for(unsigned int i=0; i<path->points.size(); i++)
0702 {
0703 gcode.writeMove(path->points[i], speed, path->config->lineWidth);
0704 }
0705 }
0706 }
0707
0708 gcode.updateTotalPrintTime();
0709 if (liftHeadIfNeeded && extraTime > 0.0)
0710 {
0711 gcode.writeComment("Small layer, adding delay of %f", extraTime);
0712 gcode.writeRetraction(true);
0713 gcode.setZ(gcode.getPositionZ() + MM2INT(3.0));
0714 gcode.writeMove(gcode.getPositionXY(), travelConfig.speed, 0);
0715 gcode.writeMove(gcode.getPositionXY() - Point(-MM2INT(20.0), 0), travelConfig.speed, 0);
0716 gcode.writeDelay(extraTime);
0717 }
0718 }End of loop through GCodePlanner::paths
src/gcodeExport.cpp#0512
src/pathOrderOptimizer.cpp#0013