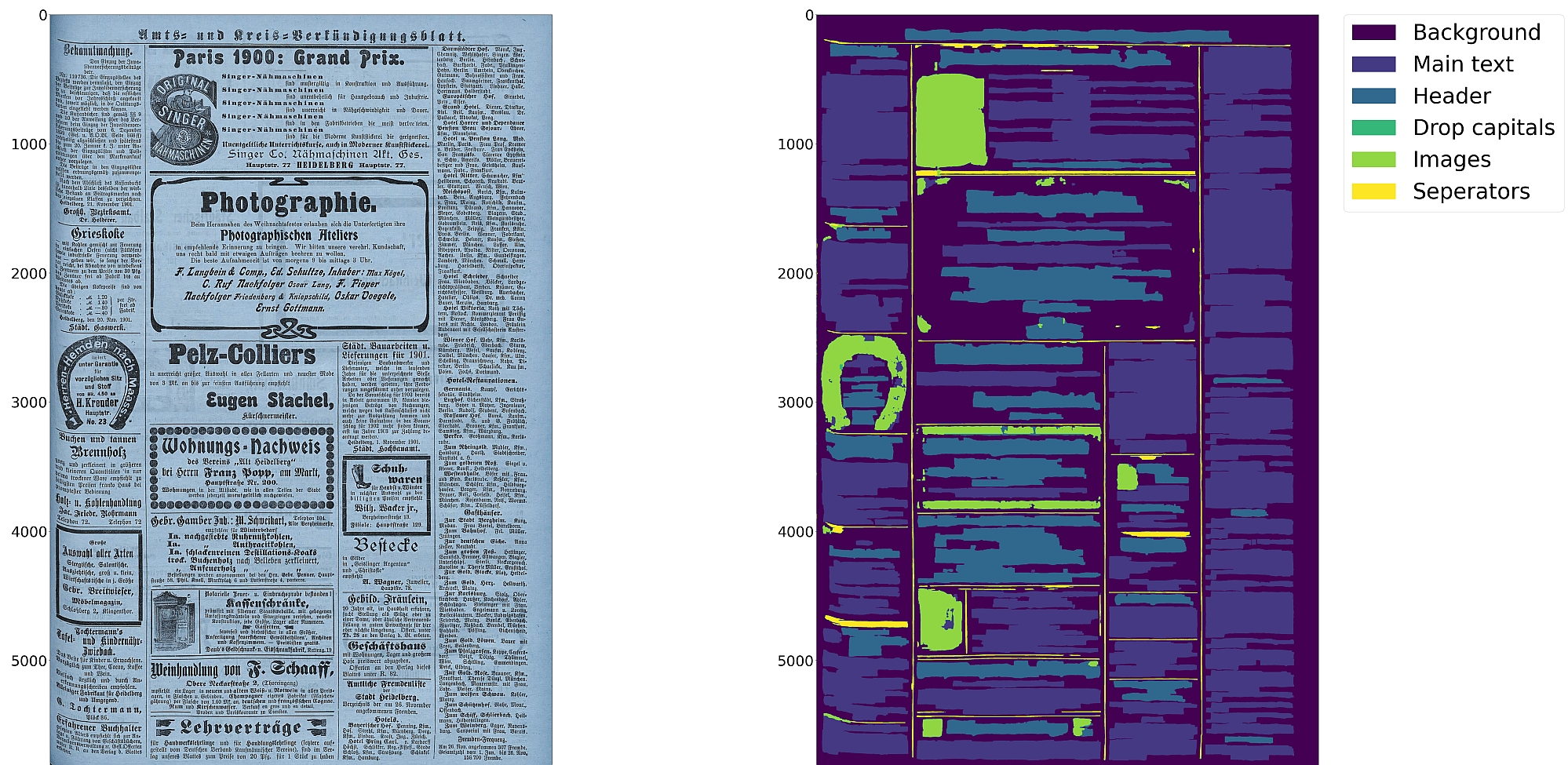
Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics
- Support for up to 10 segmentation classes:
- background, page border, text region, text line, header, image, separator, marginalia, initial, table
- Support for various image optimization operations:
- cropping (border detection), binarization, deskewing, dewarping, scaling, enhancing, resizing
- Text line segmentation to bounding boxes or polygons (contours) including for curved lines and vertical text
- Detection of reading order (left-to-right or right-to-left)
- Output in PAGE-XML
- OCR-D interface
Python 3.8-3.11 with Tensorflow <2.13 on Linux are currently supported.
For (limited) GPU support the CUDA toolkit needs to be installed.
You can either install from PyPI
pip install eynollah
or clone the repository, enter it and install (editable) with
git clone [email protected]:qurator-spk/eynollah.git
cd eynollah; pip install -e .
Alternatively, you can run make install or make install-dev for editable installation.
Pre-trained models can be downloaded from qurator-data.de or huggingface.
🚧 Work in progress
In case you want to train your own model, have a look at sbb_pixelwise_segmentation.
The command-line interface can be called like this:
eynollah \
-i <single image file> | -di <directory containing image files> \
-o <output directory> \
-m <directory containing model files> \
[OPTIONS]The following options can be used to further configure the processing:
| option | description |
|---|---|
-fl |
full layout analysis including all steps and segmentation classes |
-light |
lighter and faster but simpler method for main region detection and deskewing |
-tab |
apply table detection |
-ae |
apply enhancement (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
-as |
apply scaling |
-cl |
apply contour detection for curved text lines instead of bounding boxes |
-ib |
apply binarization (the resulting image is saved to the output directory) |
-ep |
enable plotting (MUST always be used with -sl, -sd, -sa, -si or -ae) |
-eoi |
extract only images to output directory (other processing will not be done) |
-ho |
ignore headers for reading order dectection |
-si <directory> |
save image regions detected to this directory |
-sd <directory> |
save deskewed image to this directory |
-sl <directory> |
save layout prediction as plot to this directory |
-sp <directory> |
save cropped page image to this directory |
-sa <directory> |
save all (plot, enhanced/binary image, layout) to this directory |
If no option is set, the tool performs layout detection of main regions (background, text, images, separators and marginals). The best output quality is produced when RGB images are used as input rather than greyscale or binarized images.
🚧 Work in progress
Eynollah ships with a CLI interface to be used as OCR-D processor.
In this case, the source image file group with (preferably) RGB images should be used as input like this:
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG -O SEG-LINE -P models
Any image referenced by @imageFilename in PAGE-XML is passed on directly to Eynollah as a processor, so that e.g.
ocrd-eynollah-segment -I OCR-D-IMG-BIN -O SEG-LINE -P models
uses the original (RGB) image despite any binarization that may have occured in previous OCR-D processing steps
Please check the wiki.
If you find this tool useful in your work, please consider citing our paper:
@inproceedings{hip23rezanezhad,
title = {Document Layout Analysis with Deep Learning and Heuristics},
author = {Rezanezhad, Vahid and Baierer, Konstantin and Gerber, Mike and Labusch, Kai and Neudecker, Clemens},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Historical Document Imaging and Processing {HIP} 2023,
San José, CA, USA, August 25-26, 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
year = {2023},
pages = {73--78},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3604951.3605513}
}