Authors: Marco Vasapollo (@vasapower) and Alessandro Mario Laganà Toschi (@alessandromlt) | [email protected]
DFO is a new concept that reshapes the way to build Decentralized Applications (DApps), enabling the creation of extendible, improvable and fixable Systems, using an approach called Smart Contract as Microservice which avoids the slow and dangerous monolythic Smart Contract development procedures.
Because of everything is completely deployed and running on the Ethereum blockchain, the need of Centralized or Distributed Servers is finally bypassed.
In DFO, every DApp functionality is a Smart Contract acting like a Microservice, which can also be stateless and therefore reusable in different applications.
Instead of directly using Smart Contracts functions, calling their specific address, in DFO you will interact with the Proxy which will keep track of the latest correct versions of all Microservices (located in different addresses) composing your DApp.
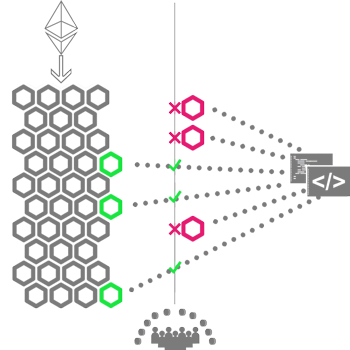
No matter how many Microservices will you attach, detach or replace to a DFO since its creation. The address of your Dapp will be always the same, forever.
DFO is completely Community Driven. This means that every strategic decision about the DApp Functionalities and their future is taken by its Token Holders. In fact, to add/replace/remove a Microservice, the proposer must interact with the Proxy to start a Survey which can be voted by the ones holding the ERC20 Voting Tokens linked to that DFO, staking them to accept or refuse the proposal. The governance rules (that establish the success or the failure of a Survey) are, in turn, Functionalities of the DFO itself located within Microservices that can be updated too... through Proposals!
The Proxy, the Voting Token, the Proposals, the Governance Rules and some other Smart Contracts are all the components that make up every single DFO.
Every DFO is a bunch of Smart Contracts cooperating each other to let users:
- using Functionalities in both Read and Write Mode;
- proposing to add/remove/replace these Functionalities through Surveys;
- voting to Accept/Refuse them through Voting Tokens.
Even the Smart Contracts of a DFO can be updated to address bug fixes or to expand the potential of the protocol just making a Proposal to the Token Holders Community.
To let people create and use DFOs, we built DFOHub, our R&D community-driven project that aims to improve the DFO protocol itself by managing its progress through a DFO maintained by its own token holders, who can propose or vote for improvements and bug fixes with anonymous, decentralized and very easy steps. DFOHub extremely facilitates the deployment processes for a new DFO, you can exploit it in two ways:
- using the easy steps of the wizard we coded on DFOHub;
- [COMING SOON] using the integration SDK which lets you easily integrate DFO protocol capabilities in your DApp.