KmerGO is a user-friendly tool to identify the group-specific sequences on two groups of high throughput sequencing datasets. A sequence that is present, or rich, in one group, but absent, or scarce, in another group is considered “group-specific” here. Furthermore, KmerGO can also be applied to capture trait-associated sequences for continuous-trait dataset.
Compared with other tools, KmerGO have the following advantages:
-
KmerGO offers both graphic user interface (GUI) under Windows & Linux and command line (CL) mode under Linux, with one-click installation free from environmental settings.
-
KmerGO is able to capture the group-specific k-mers (k up to 40bps) for categorical dataset and trait-associated k-mers for continuous-trait dataset with much lower requirements for computing resource in much shorter running time.
-
Users can run KmerGO by one-click mode or step-by-step mode and use the output group-specific k-mers or sequences to be the input of other tools for the following discovery of biomarkers, such as genetic variants, species or genes.
In our experiment, through multi-processes parallel computing, KmerGO is able to capture all the group-specific k-mers (k up to 40bps) for 1.07 TB data in fasta format on a regular standalone server(Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5-2620 v4 @ 2.10GHz) in 21.5 hours, including 4 hours Kmer counting with KMC[http://sun.aei.polsl.pl/REFRESH/kmc] and 17.5 hours(16 processes number) group-specific kmer identification, and return the assembled group-specific sequences.
Github for KmerGO(v2.x.x) which is a faster version is here.
Please cite: Wang Y, Chen Q, Deng C, Zheng Y and Sun F (2020) KmerGO: A Tool to Identify Group-Specific Sequences With k-mers. Front. Microbiol. 11:2067. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02067
KmerGO can be run directly on Windows and Linux operating systems, without extra enviromental settings or configurations.
KmerGO has been tested on Windows 7/8/10 (64 bits).
And you can click here to download the Windows version of KmerGO.
Decompress the file and run the "Install.bat" with the highest authority if you first use KmerGO.
After that, you can double-click KmerGO.exe to run it.
KmerGO has been tested on Ubuntu 16, Debian 9, CentOS 7, Fedora 30 and Deepin 15 (64 bits).
-
Download the Linux GUI version of KmerGO: download link.
-
Download the Linux command version of KmerGO: download link.
Decompress the file and enter the software path.
Type these commands if you first use KmerGO:
sudo chmod +x KmerGO
sudo chmod +x ./bin/*
- For GUI version:
You can type ./KmerGO to run it.
- For CMD version:
You can type ./KmerGO [optional options] -i <input_files_folder> -t <input_trait_information> to run it.
We prepared some FASTA format files which are stored in "test_data/samples".
And trait files can be also found in folder "test_data".
Because the small size of testing data, "k=25 MinValue=1" and other parameters as defaults are recommended.
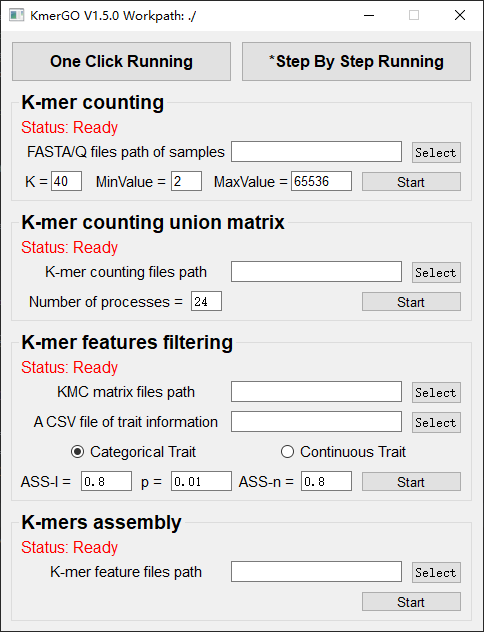
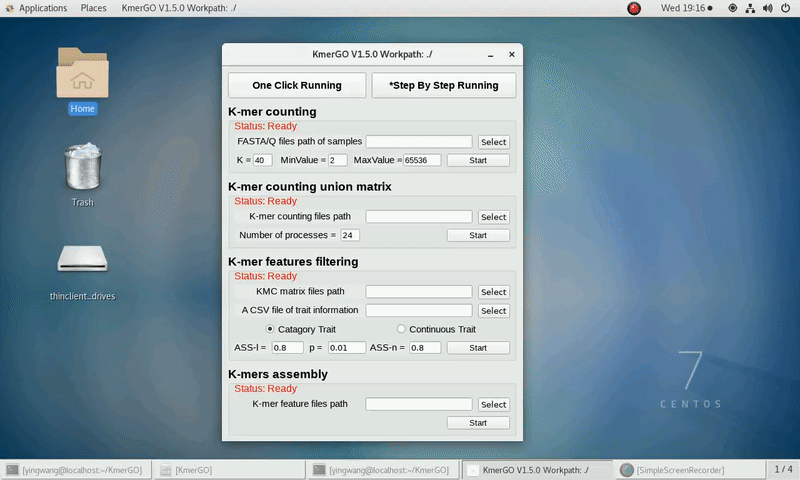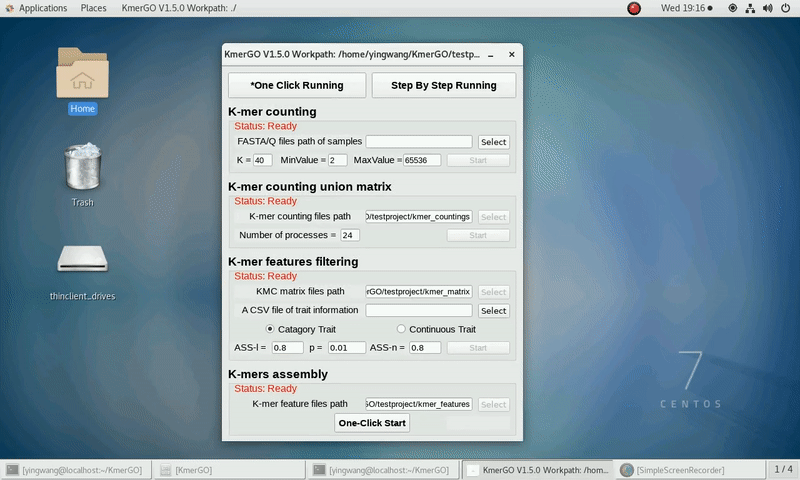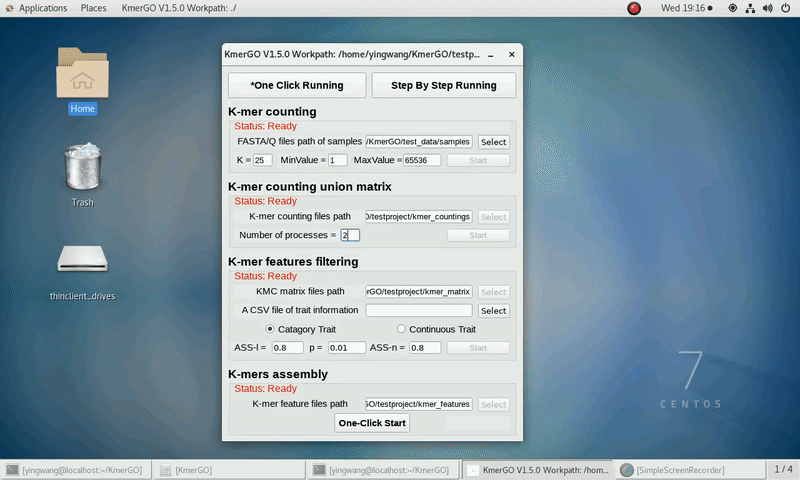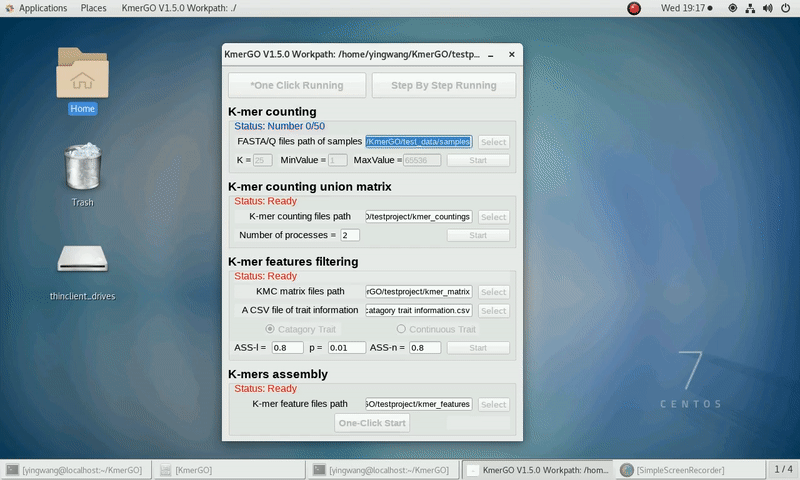
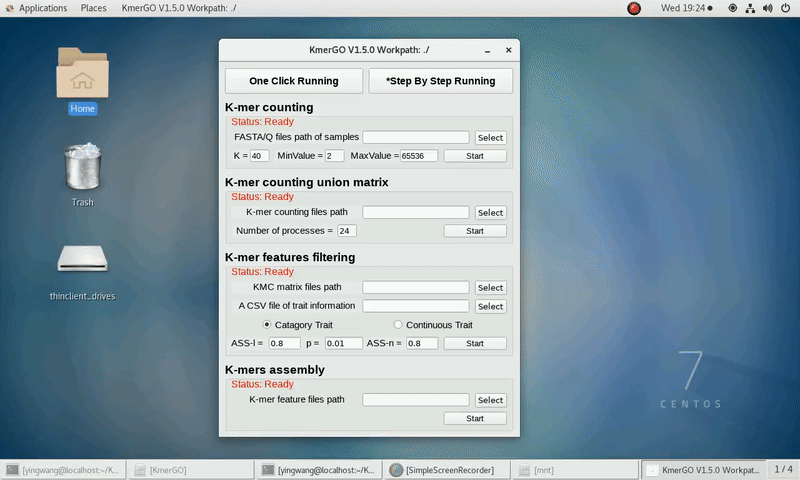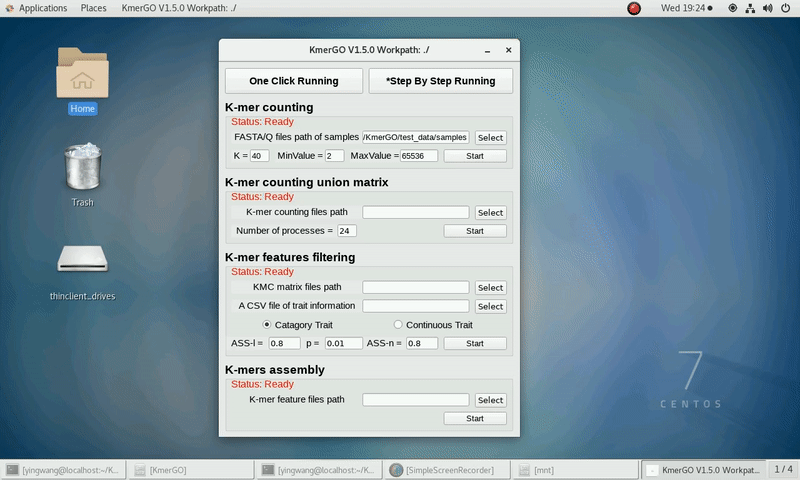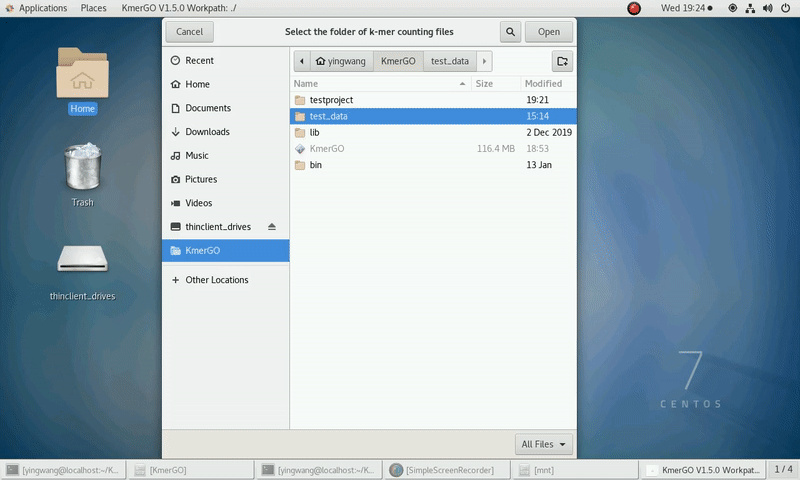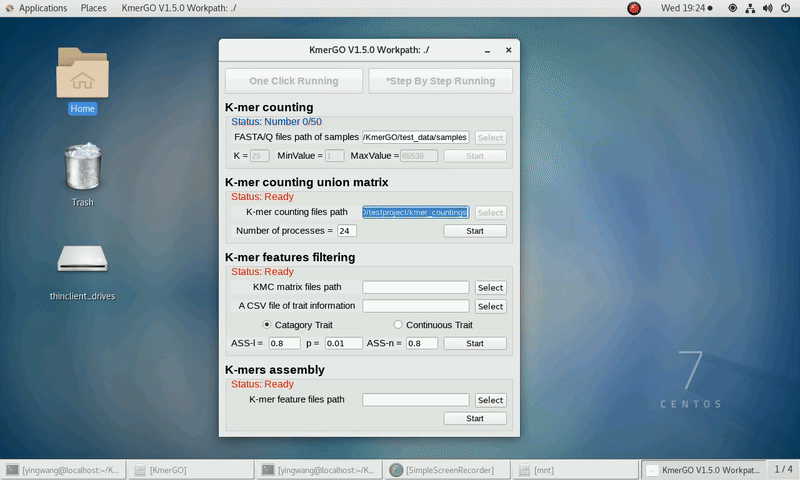
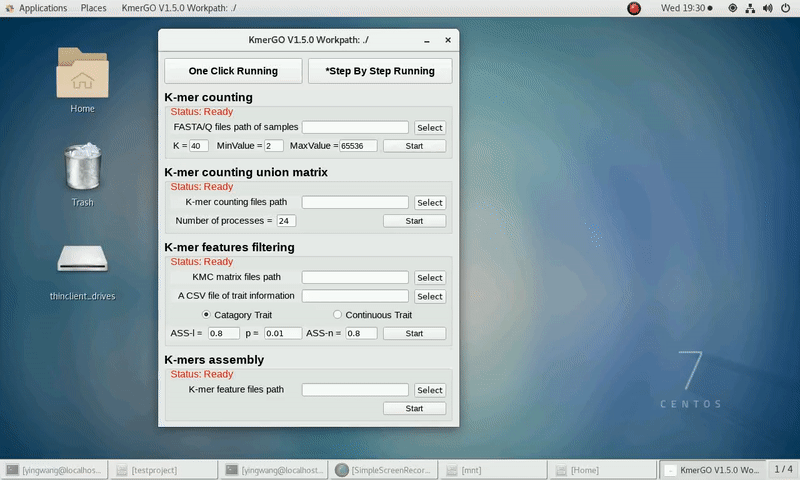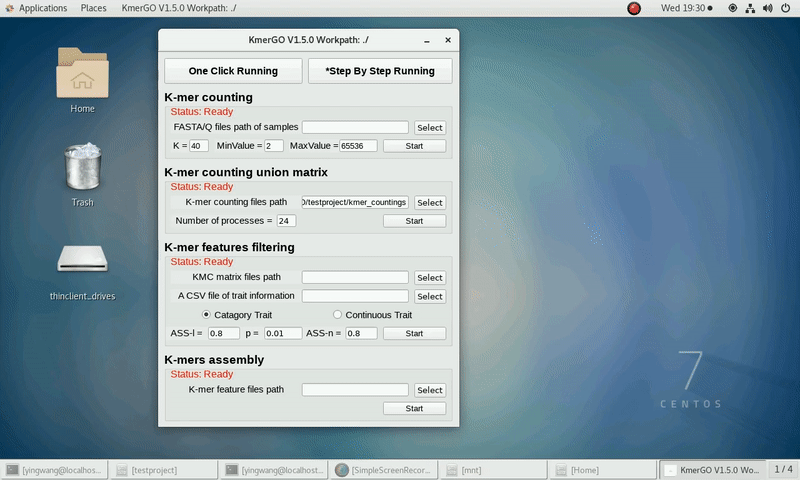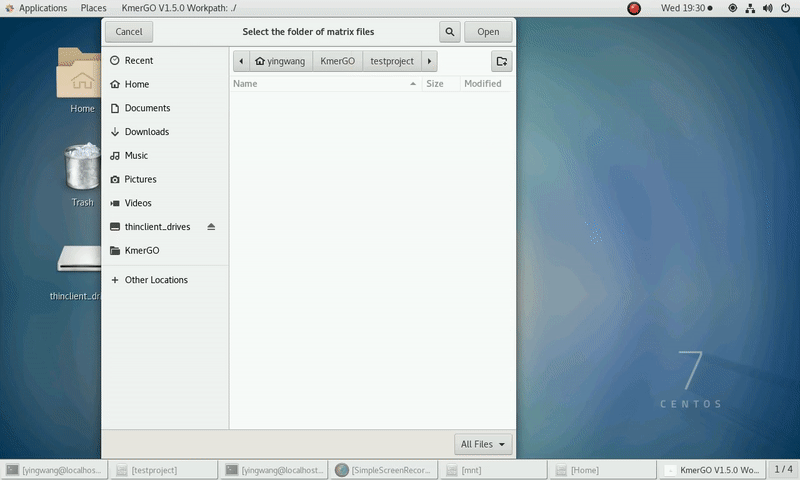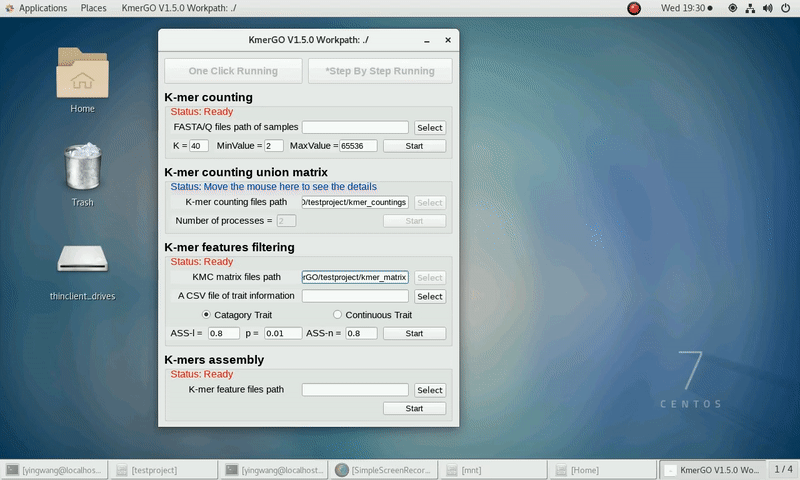
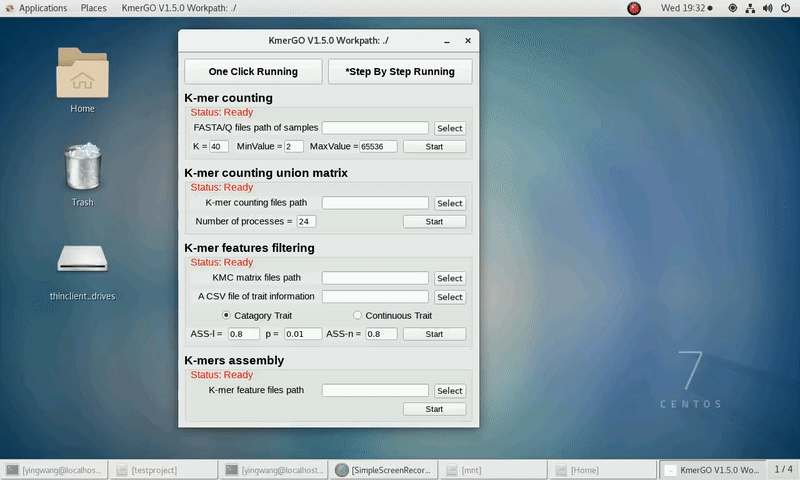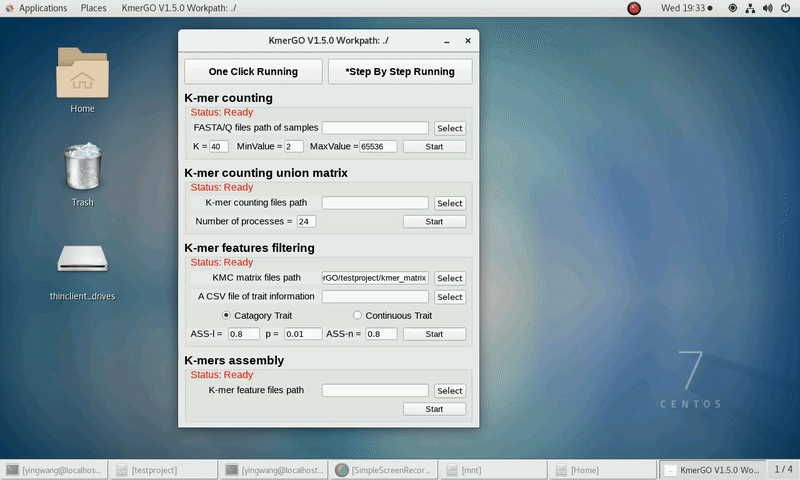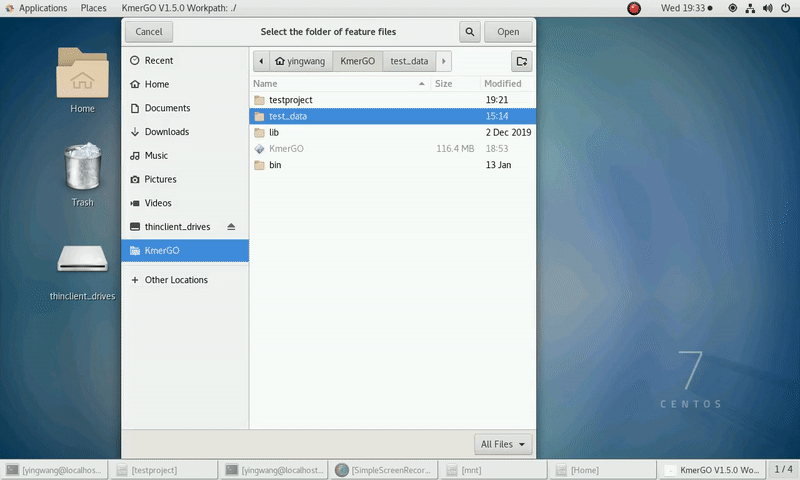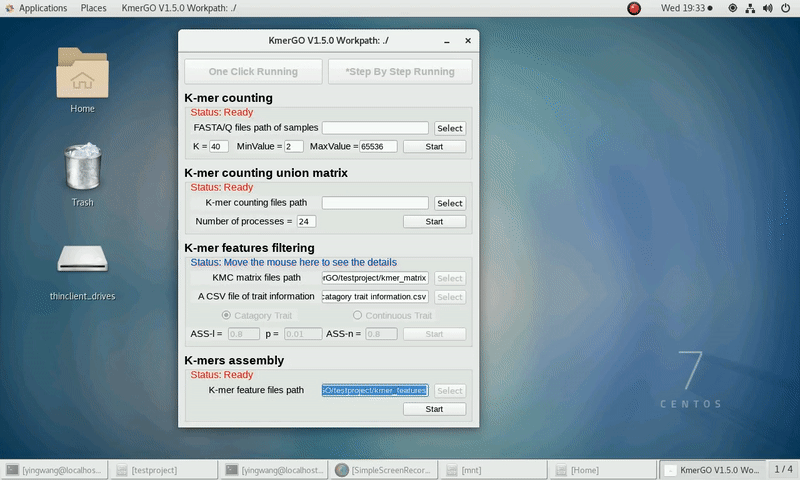
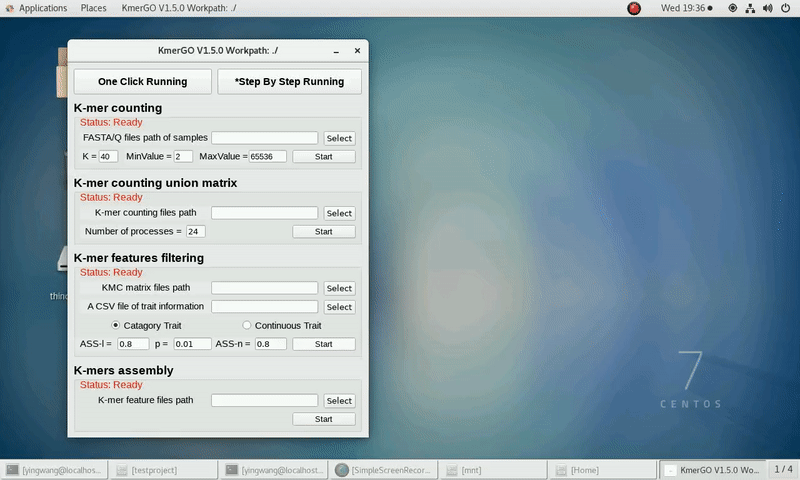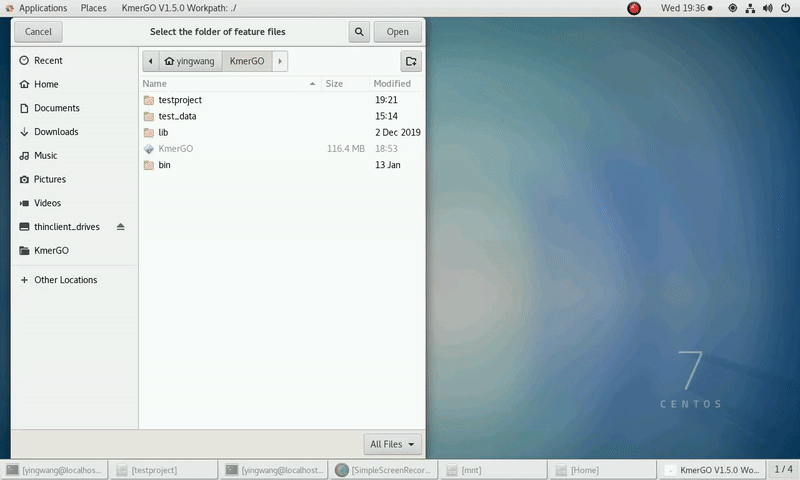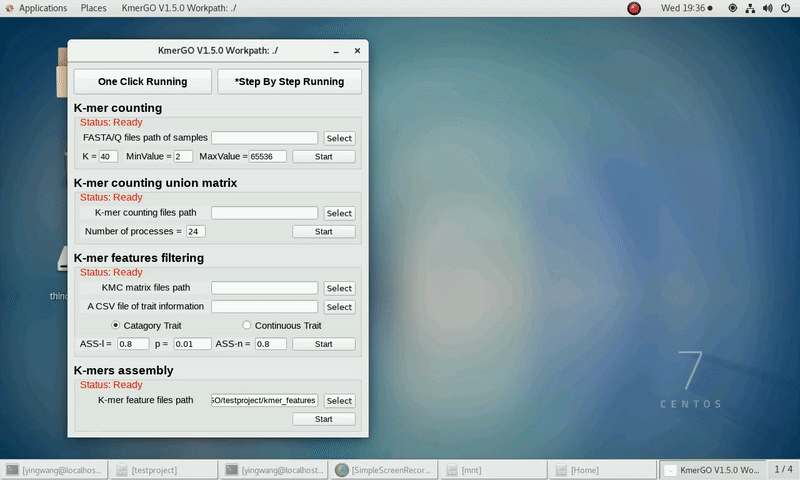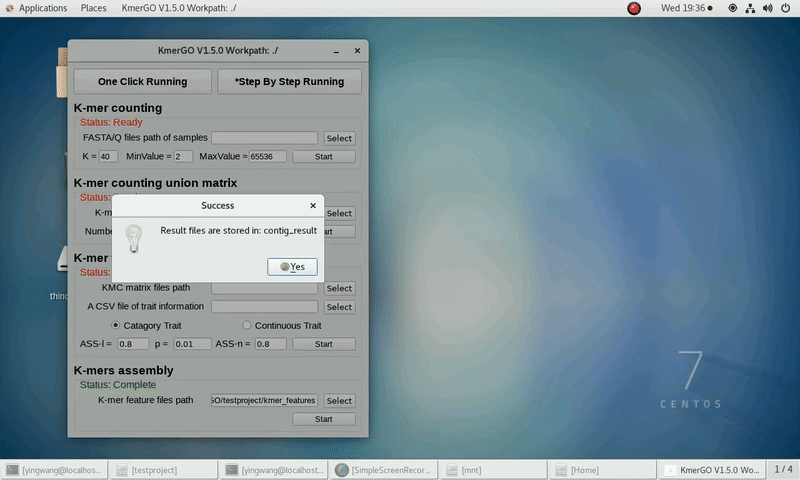
There are four modules in KmerGO: 1.K-mer counting, 2.K-mer counting union matrix, 3.K-mer features filtering, 4.K-mers assembly. And you can use one-click running to identify the group-specific sequences or separate-module running to obtain some midway results.
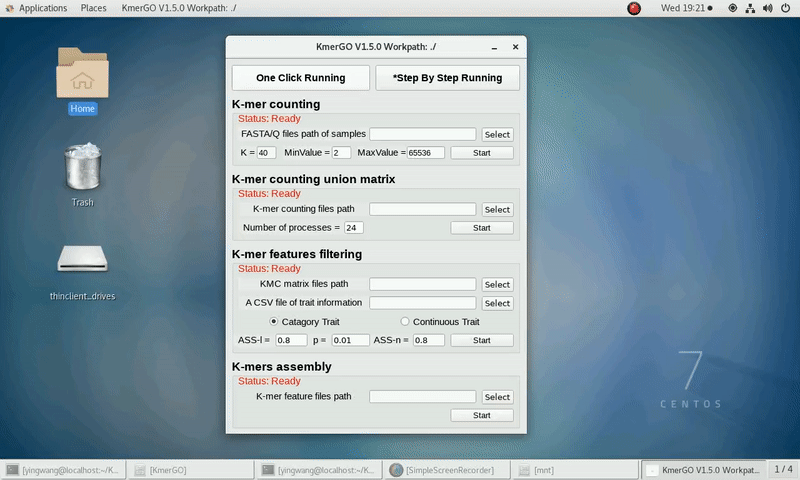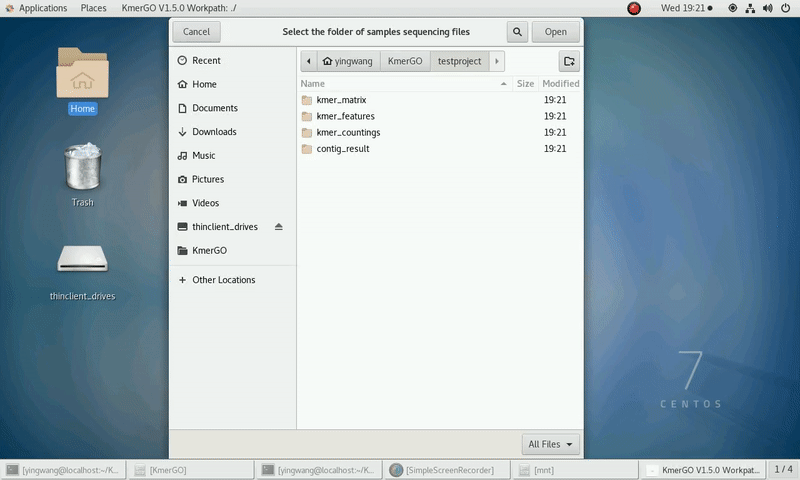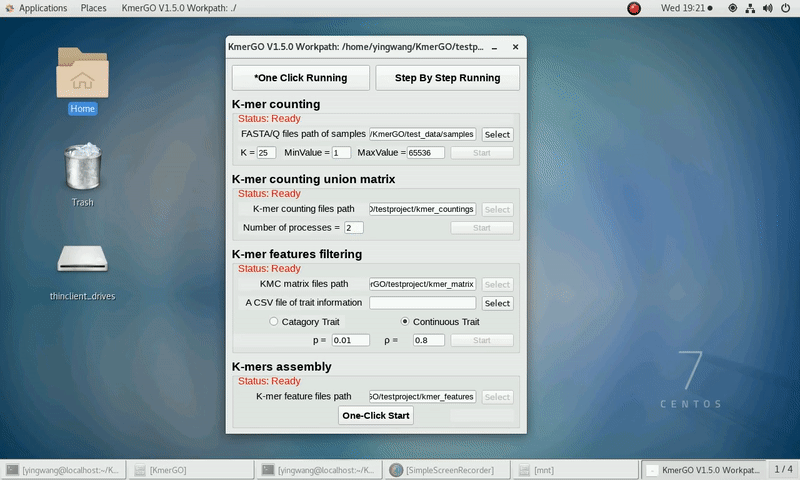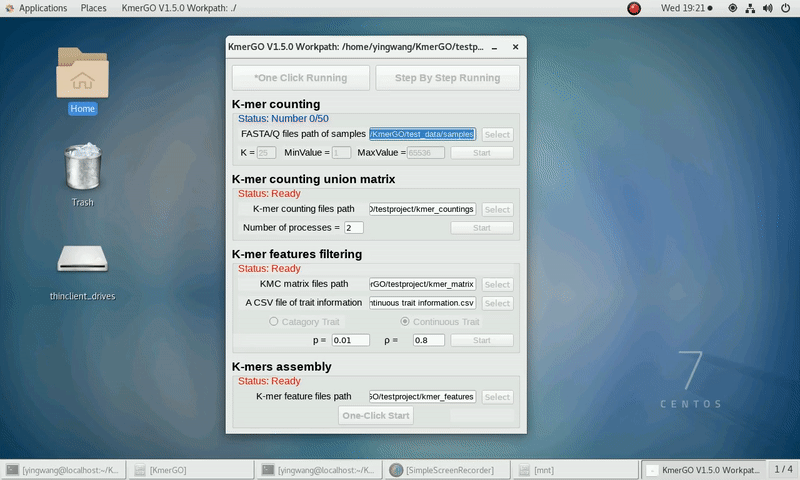
As shown in the following Gif, You should first select a workpath folder of work path. KmerGO will produce all step results under the work path.
After that, you can set the parameters and press the button "One-Click Start" to start the running. KmerGO can execute all steps automatically if there are no errors.
a) categorical trait type
b) continuous trait type
And the result files will be created in "{$workpath}/contig_result" folder.
1. K-mer counting
If you want obtain the K-mer occurring times using the short reads of FASTA/Q format files independently, you can set it up according to the following steps:
(1) Select "FASTA/Q files path of samples" of input files path.
(2) Select "K-mer counting files path" of output files path.
(3) Set K-mer length (K), K-mer occurring times lower value (MinValue) and K-mer occurring times upper value (MaxValue).
(4) Click "Start" button to run it.
2. K-mer counting union matrix
If you want obtain the K-mer matrixes in different samples using sorted K-mer occurring times independently, you can set it up according to the following steps:
(1) Select "K-mer counting files path" of input files path.
(2) Select "KMC matrix files path" of output matrixes path.
(3) Set the number of processes.
(4) Click "Start" button to run it.
3. K-mer features filtering
If you want obtain the K-mer filtering features using the K-mer union matrixes independently, you can set it up according to the following steps:
(1) Select "KMC matrix files path" of input matrixes path.
(2) Select the trait type (categorical or continuous).
(3) Select "A CSV file of trait information".
(4) Select "K-mer feature files path" of output features path.
(5) Set ASS threshold value of logical features, rank sum test p value and ASS threshold value of numerical features. Or Set rank sum test p value of logical features and spearman ρ threshold value of numerical features.
(6) Click "Start" button to run it.
4. K-mers assembly
If you want obtain sequences assembly using the K-mer features independently, you can set it up according to the following steps:
(1) Select "KMC feature files path" of input features path.
(2) Click "Start" button to run it.
(3) The result files will be created in "contig_result" folder.
Now, command version of KmerGO only has END-TO-END mode. The main running command is ./KmerGO with following options:
| short option | long option | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| -h | --help | No | show the help message and exit |
| -i | / | Yes | sample files path |
| -t | / | Yes | a csv file path of trait information |
| -m | --mode | No | mode: 0-categorical, 1-continuous (default: 0) |
| -k | --kmerlength | No | k-mer length (k from 14 to 256; default: 40) |
| -ci | / | No | minimal K-mer occurring times (default: 2) |
| -cs | / | No | maximal K-mer occurring times (default: 65535) |
| -n | / | No | number of processes (default: 24) |
| -assl | / | No | when mode = 0, logical features ASS value (default: 0.8) |
| -p | / | No | numeric(mode=0) or logical(mode=1) features rank sum test p threshold value (default: 0.01) |
| -assn | / | No | when mode = 0, numeric features logistic regression ASS value (default: 0.8) |
| -corr | / | No | when mode = 1, numeric features coefficient of association ρ threshold value (default: 0.8) |
Example: ./KmerGO -k 25 -ci 1 -n 2 -i ./test_data/samples/ -t ./test_data/categorical\ trait\ information.csv
Categorical Trait
Example1:
id,trait
1,A
2,A
3,B
...
Example2:
id,trait
SRR1,Case
SRR2,Control
SRR3,Case
...
Continuous Trait
Example:
id,trait
SRR1,1.02
SRR2,2.35
SRR3,5.22
...
Templates can be also found in the folder "test_data".
KmerGO will normalize the K-mer counting to the level of 10^-4 and output the normalization coefficients of each sample at the "Module 2".
Pair-end sequencing data is now supported by KmerGO(version >= 1.5.0b1). You can use the following file format:
A1.fasta.gz A1_1.fasta.gz, A2.fasta.gz A2_1.fasta.gz, ... , B1.fasta.gz B1_1.fasta.gz, ...
Please send bug reports, comments, or questions to here.
or email to
Prof. Ying Wang: [email protected]
Wenhao Zhang: [email protected]
Last update: 2023-03-06